Chest infections can range from mild to severe, affecting the lungs and airways and leading to symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Proper chest infection management is essential to ensure a swift recovery and to prevent complications, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and individuals with chronic health conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective care.
Chest infections are typically classified into two main types: bronchitis and pneumonia. Bronchitis involves inflammation of the airways and is commonly caused by viral infections, though it can sometimes be bacterial. Pneumonia, on the other hand, affects the lung tissue itself and is more often bacterial in origin, though viruses can also be responsible. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the individual’s overall health, age, and the type of infection.
Early identification of symptoms plays an important role in managing chest infections. Common signs include a persistent cough, increased production of mucus, wheezing, fever, chest pain, and fatigue. In some cases, individuals may experience difficulty breathing or a bluish tint to the lips and fingernails, indicating a more serious problem that requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment approaches depend on the underlying cause and severity of the infection. For viral bronchitis, supportive care such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms is usually sufficient. If a bacterial infection is suspected, a healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
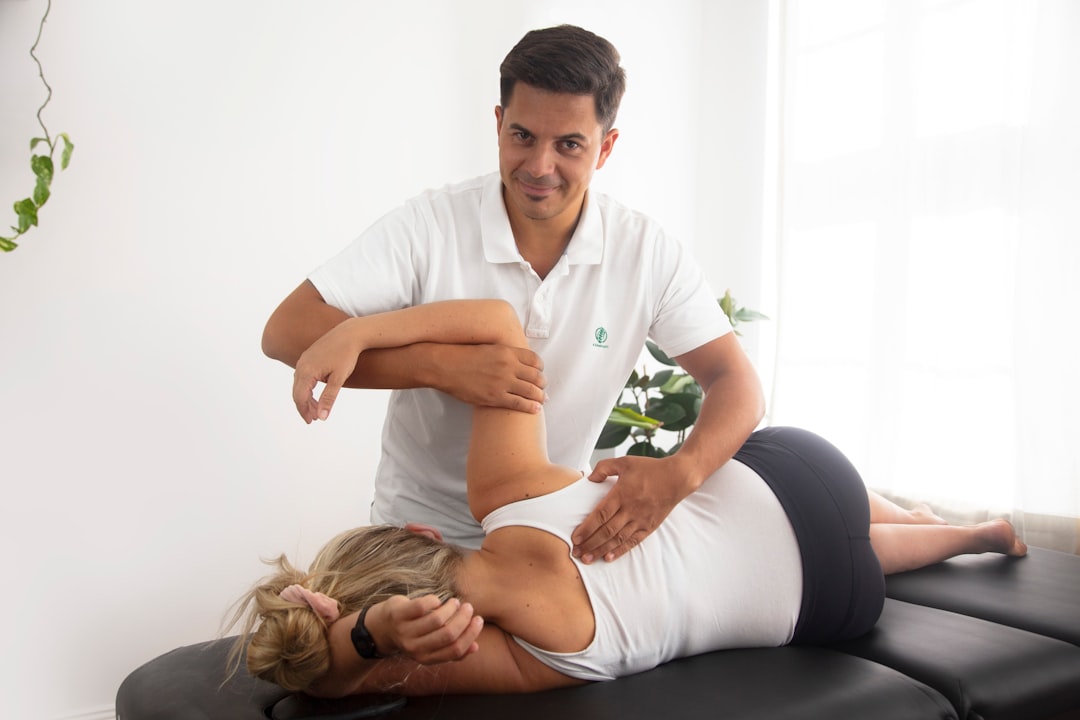
In addition to medication, physiotherapy can play a valuable role in recovery. Techniques such as chest physiotherapy help loosen mucus in the lungs, making it easier to cough up. This can be especially helpful for individuals with underlying respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Physiotherapists can also guide patients through breathing exercises to improve lung function and reduce breathlessness. Engaging with professional services such as chest infection management can support a faster and more complete recovery.
Maintaining good hygiene is key to preventing the spread of infections. Regular handwashing, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals are effective preventive measures. For those with weakened immune systems or chronic respiratory diseases, vaccination against flu and pneumonia is recommended to reduce the risk of serious infections.
Environmental factors also influence respiratory health. Exposure to cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational irritants can increase susceptibility to chest infections and prolong recovery times. Smoking cessation and reducing exposure to pollutants are important lifestyle changes that can improve lung health and resilience against infection. Adequate nutrition, regular exercise, and proper sleep also contribute to a stronger immune system, which is essential in both preventing and recovering from respiratory illnesses.
It is not uncommon for individuals to delay seeking medical advice, often assuming symptoms will resolve on their own. However, left untreated, chest infections can lead to complications such as pleurisy, lung abscesses, or respiratory failure, particularly in high-risk groups. Therefore, any persistent or worsening symptoms should be assessed by a healthcare provider without delay.
Some individuals may benefit from ongoing physiotherapy even after the acute phase of the infection has passed. This can help restore full lung function, reduce the risk of recurrence, and manage any residual symptoms. Services focusing on respiratory physiotherapy support can be particularly valuable during the recovery period and for those with chronic conditions.
Managing a chest infection effectively involves a combination of timely medical intervention, supportive therapies, and lifestyle adjustments. By addressing symptoms early and engaging in comprehensive care, individuals can reduce recovery time and minimise the impact of chest infections on daily life. Ongoing education and awareness about prevention and management strategies remain central to reducing the burden of respiratory infections in the community.